Should the conversion of $98 million of individual labor compensation income to business income be characterized as tax evasion?
Recently, a Notice of Tax Administrative Penalty Matters has attracted wide attention, in which a natural person converts the nature of income by setting up a sole proprietorship enterprise, and draws up tax evasion and imposes a fine of 15.91 million yuan. In the past, in the field of network entertainment, there have been many cases of fictitious business, converting income from remuneration for labor services to business income, and converting income from domestic individuals to income from overseas enterprises, and the tax-related risk of converting the nature of income is still high. This article intends to analyze the way of realizing tax benefits and tax-related risks by converting the nature of income in the light of the case, and further put forward the compliance points of avoiding tax burden by adopting such a way.
Ⅰ. Introduction of the Case: Conversion of Income by Sole Proprietorships
On May 12, 2023, the Inspection Bureau of S Municipal Taxation Bureau issued a Notice of Tax Inspection to Zhang Mou to inspect his tax-related situation from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2022. It was found that from 2020 to 2021, Company A and Zhang entered into the Financial Consultant Service Agreement, agreeing that Company A would pay consulting labor remuneration of RMB98.03 million to Zhang, of which RMB52.89 million would be paid in 2020 and RMB45.14 million would be paid in 2021. During the period, Zhang set up two sole proprietorships, B Consulting Center and C Consulting Center, and Company A entered into the Supplemental Agreement to the Financial Consulting Service Agreement with the two sole proprietorships, through which its remuneration for the aforesaid consulting services was paid to the two sole proprietorships.
The tax authorities considered that Zhang converted the nature of his income by setting up a sole proprietorship enterprise, converted the income from labor remuneration received by an individual into the income from the operation of a sole proprietorship enterprise, and made false declarations, resulting in underpayment of individual income tax, which was tax evasion. Zhang should declare and pay 34.98 million yuan of comprehensive income individual income tax from 2020 to 2021, and Zhang has declared and paid 3.16 million yuan of comprehensive income individual income tax, under-declaring and paying 31.82 million yuan of comprehensive income individual income tax. According to the provisions of Article 63(1) of the Tax Collection and Administration Law, Zhang was proposed to be subject to a fifty percent fine of 15.91 million yuan for the underpayment of consolidated income individual income tax of 31.82 million yuan.
According to public information, the two sole proprietorships used by Zhang to convert the nature of his income were written off on March 4, 2022 and July 27, 2022, respectively.
Ⅱ. How can the conversion of the nature of income avoid the tax burden?
"Converting the nature of income" refers to the establishment of sole proprietorships and partnerships in tax pockets, converting the comprehensive income of individuals such as salaries and wages and remuneration for services into business income, and at the same time utilizing tax incentives such as local tax exemptions and exemptions, approved levies, and rebates from the local treasury in order to reduce the tax burden. As a common means for HNWIs to avoid tax burden, "conversion of income nature" mainly utilizes the differences in tax rates of different income natures and various tax incentives to realize tax benefits.
(Ⅰ) The nature of income obtained by an individual through the provision of labor services by a sole proprietorship enterprise is unknown.
From the provisions of the Regulations for the Implementation of the Individual Income Tax Law, the scope of income from labor remuneration and business income adopts the legislative model of "positive enumeration + underlining provisions", which mainly specifies the types of services provided by the labor for the income from labor remuneration, reflecting the "content" level; but for the business income, it mainly takes advantage of the differences in the nature of different incomes and various tax preferences to realize tax benefits. "However, for business income, it is classified in terms of the form of the main body engaged in production and business, therefore, the relevant provisions of the individual income tax do not completely clarify the boundaries of the remuneration for labor services and business income. This has led to greater controversy in practice as to whether the income derived from the provision of labor services by an individual setting up a sole proprietorship enterprise belongs to operating income.
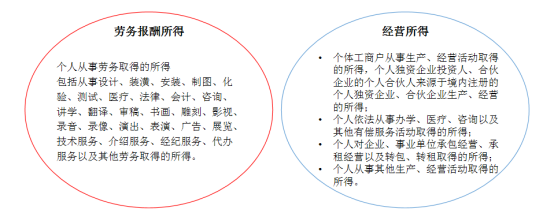
There is a view that, for some of the strong personal dependence of labor behavior can only be completed by the individual, can not be contractually agreed to change the behavior of the business essence, also can not be signed by the subject of the contract, the books of accounts and other legal forms and change the nature of the income received. For example, the network anchor engaged in live with goods type of labor with obvious personal dependence, the commissioner whether cooperation, the audience whether to buy are very dependent on the anchor personal appearance, image, word of mouth and other elements, so the anchor thus obtained commission from the economic substance can only be the anchor personal marketing services obtained by the consideration, i.e., remuneration for labor income. There are also views that the law does not prohibit the unit as the main body of the provision of labor services, the unit's employees, investors actually complete the labor activities, does not affect the unit to become a legal provider of labor services, the taxpayer's choice of mode of transaction belongs to the civil category of autonomy, the tax authorities do not have the right to intervene in the income has not yet occurred in advance to intervene in the taxpayers' civil law behavior, so the taxpayer chooses to provide labor services and receive remuneration through its sole proprietorship, it is the taxpayer who chooses to provide labor services and receive compensation. Therefore, the taxpayer's choice of providing labor services and receiving remuneration through his/her sole proprietorship enterprise is within his/her autonomy, and also belongs to the reasonable tax planning within the framework of the law. As to whether the labor service activities and remuneration received by an individual through a sole proprietorship enterprise belong to business income, there is no clear legal provision on the demarcation and judgment standard, and the tax authorities have not formed a unified enforcement caliber. In practice, converting the nature of income has become a common means of tax planning for HNWIs.
(Ⅱ) Different tax burden between labor remuneration income and business income
According to the Individual Income Tax Law, the income from remuneration for labor services is a comprehensive income, and an individual who obtains a comprehensive income can confirm the taxable income by deducting the income for each tax year from 60,000 yuan, as well as the balance of special deductions, special additional deductions and other deductions determined in accordance with the law, and applying the excessively progressive tax rate ranging from 3% to 45%. As for the business income, it is the income obtained from the business activities of the taxpayers who set up individual industrial and commercial households, sole proprietorships, partnerships, etc. The taxable income should be recognized by the total income of each tax year minus the balance of costs, expenses and losses, and the ultra-progressive tax rate of 5% to 35% is applied. It can be seen that, compared with the income from labor remuneration, the operating income is more favorable in terms of expense deduction, and the highest level of the applicable tax rate is also relatively low, in the case of higher income, the conversion of the income from labor remuneration to the operating income can play a role in circumventing the effect of the tax burden.
(Ⅲ) Utilizing local tax incentives to reduce tax burden
The reason why subjects such as sole proprietorship enterprises are easily used to implement profit shifting also lies in the fact that, in the past, due to the lack of guidance from the superior law, local governments, in order to promote investment promotion, existed the phenomenon of providing tax incentives such as approved levies or fiscal refunds to locally registered enterprises, and that individuals, by converting the income they actually earn into business income, were able to significantly reduce their comprehensive tax burden, thus realizing the benefits of taxation. However, with the tightening of the application space of approved levy and the centralized clean-up of improper local tax incentives and fiscal rebate policies, the tax potholes are gradually being "filled up".
Ⅲ.Tax-related Risks of Converting the Nature of Income
(Ⅰ) Conversion of income is easily characterized as tax evasion.
According to Article 63(1) of the Tax Collection and Management Law and the relevant tax normative documents of the State Administration of Taxation on the determination of tax evasion, a taxpayer shall subjectively have the intention of tax evasion and objectively commit tax evasion and cause the consequence of non-payment or underpayment of tax. If an individual directly signs contracts, conducts business and obtains income in his/her name, and then establishes a sole proprietorship enterprise only for the consideration of tax benefits, and adjusts the sole proprietorship enterprise as a business subject, but these enterprises are shell companies, there is no actual operation, and even the content of the service agreement itself is false, it is very easy for the tax authorities to recognize this kind of fictitious business and conversion of the nature of the income as "making false tax declarations". The taxpayer will not only be required to pay back taxes and late fees, but will also be liable for a fine of not less than 0.5 times and not more than 5 times the amount of unpaid or underpaid taxes. If the taxpayer is unable to pay the back taxes, late fees and fines in accordance with the law, the administrative liability may also be transformed into criminal liability for tax evasion.
(Ⅱ) Implicated Tax Risks of Written-off Individual Sole Proprietorships
According to the Sole Proprietorship Law, the investor shall bear unlimited liability for the debts of the enterprise with his personal property. Individual sole proprietorship enterprise dissolution write-off, the liquidation of the individual sole proprietorship enterprise property is not enough to settle debts, the investor shall be its personal other property to be paid. Therefore, if a sole proprietorship enterprise is found to have underpaid tax, even if it has been canceled, the tax authorities still have the right to recover the unpaid tax from the investor.
Ⅳ.Whether the conversion of the nature of income should bear legal responsibility
(Ⅰ) "Conversion of the nature of income" does not necessarily have to make tax adjustments
Tax avoidance refers to the use of tax law loopholes, differences and blind spots, to avoid, reduce or delay the performance of tax obligations are not illegal behavior. In tax avoidance behavior, the taxpayer adopts a special transaction mode, which makes the tax obligation of the relevant transaction lower than the tax obligation under the usual transaction mode. In response to the tax avoidance behavior, the tax law gives the tax authorities the right of tax adjustment. According to Article 35(1)(6) of the Tax Collection and Administration Law, tax adjustment for tax avoidance behavior needs to satisfy two major conditions, one is that the tax basis is obviously low, and the other is that the taxpayer does not have justifiable reasons.
In this case, although Zhang realized the effect of large-scale tax saving by converting the nature of income, it is still necessary to examine whether there are justifiable reasons for the design of this transaction mode. If the two sole proprietorship enterprises established by Zhang Mou are entity enterprises with actual business, and the parties agree to adjust the subject of the contract from Zhang Mou to a sole proprietorship enterprise for reasonable business purposes such as business compliance and easy accounting, and the sole proprietorship enterprise actually fulfills the obligations agreed in the contract, and the relevant results of the work are fully embodied in the implementation of the sole proprietorship enterprise, the two parties are based on the principle of self-government to change the transaction mode, and the tax authorities should not arbitrarily deny and adjust the transaction mode. The tax authorities should not arbitrarily deny and adjust.
(Ⅱ) "Conversion of the nature of income" does not necessarily constitute a false tax declaration of tax evasion.
Even if the tax authority determines that there is underpayment of tax in the nature of conversion of income, which needs to be adjusted for tax payment, it can't be characterized as tax evasion, and tax evasion must comply with the legal constituent elements. According to the Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Specific Application of Law in the Trial of Criminal Cases of Tax Evasion and Tax Resistance (Legal Interpretation [2002] No. 33), Article 2, Paragraph 3, "False Tax Declaration" refers to the taxpayers' fabrication of false contracts, documents, qualification certificates, and other tax-related basic information and account books, vouchers, statements, and other financial and tax record information, which will be used to make these false information and its reflection. False tax declaration" means that taxpayers fabricate false tax-related basic information such as contracts, documents and qualification certificates, and financial and tax records such as account books, vouchers and statements, and report such false information and the false taxable data reflected therein to the tax authorities, so as to obtain unlawful tax benefits, such as non-payment, underpayment, tax reduction and exemption. From the principle of subjective and objective consistency, the composition of "false tax returns" should meet:
1、The taxpayer subjectively fraudulent fault, that is, fictitious, concealment of the truth, to deceive the tax authorities on purpose;
2、The taxpayer has committed fraud, that is, the tax return information with the objective facts are obviously inconsistent.
According to Article 25 of the Tax Collection and Administration Law, "taxpayers must truthfully handle tax declaration in accordance with the provisions of laws and administrative regulations or the tax authorities in accordance with the provisions of laws and administrative regulations to determine the declaration period and the content of the declaration, and submit tax declaration forms, financial and accounting statements, as well as the tax authorities in accordance with the actual needs of the taxpayers required to submit other tax information ". That is, the taxpayer has to the tax authorities on schedule, truthfully declare and report the tax information of the concerted obligation, as long as the taxpayer to provide tax information with the objective facts, there is no deception and concealment behavior, it is not a false tax declaration behavior. As for the taxpayer should be in accordance with what kind of tax items, tax rate to pay taxes, belong to the application of the tax law, the tax authorities should be based on tax information and objective facts to review and make conclusions. If the conclusion of the tax authority is inconsistent with the conclusion of the taxpayer, it is a different understanding of the application of the tax law, and the tax authority can make tax adjustments, but cannot be characterized as tax evasion.
Ⅴ. Tax Compliance: Strengthening the Business Purpose of Substantial Operations and Transactions
For individuals to provide labor services or services, but in the name of a sole proprietorship enterprise to obtain and pool the income, should not be a blanket conversion of the nature of the income only on the grounds of characterization of tax evasion, and should pay attention to the implementation of the conversion of the behavior of the income has actually occurred, the existence of the enterprise's actual operation and the actual business purposes of both sides of the business.
As mentioned above, if the taxpayer solicits business and carries out business activities in the name of the enterprise, and the enterprise is not a "shell enterprise", it should be recognized that there is substantial business operation, and the taxpayer's business in this mode is in compliance with the provisions of the tax law, and should not be adjusted for tax. Specifically, whether the enterprise constitutes substantial business, should be around the following aspects to determine:
1、Production and operation: whether the enterprise has actual production and operation places, whether it has production and operation, accounts, personnel and other related decision-making, implementation of procedures and conditions.
2、Personnel: the existence of the actual work of the enterprise employees, wages and salaries are issued through the bank account opened by the enterprise.
3、Financial: whether the enterprise exists independent accounting documents, accounting books and financial statements and other archives, whether there is a bank account specializing in the settlement of the main business.
4、Assets: whether there are necessary assets held in the name of the enterprise for the purpose of carrying out production and business activities.
Furthermore, in the case of a sole proprietorship enterprise where there is an actual business operation, if the taxpayer reaches an agreement with the counterparty before the business is actually carried out, and changes the party providing labor or services from a natural person to an enterprise for a reasonable commercial purpose, the result of party autonomy should be respected to confirm the fact of the transaction that the enterprise performs its contractual obligations to the counterparty, and it is not appropriate to make tax adjustments to the taxpayer.