What are the differences between the views of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate on the four types of crimes of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT?
Introduction
Document No.30 of Fa [1996], which has expired, once classified the crime of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT into three categories.They are false opening without goods, false opening with goods with inconsistent quantity or amount, and truthful opening on behalf of others.The first paragraph of Article 10 of the tax-related judicial interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate, which came into effect on March 20 this year, is "enumeration + bottom-up".The way reconstructs the different situations of the crime of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT.It clearly lists four types of criminal acts, namely, false opening without goods, false opening with goods, false opening of fictitious subjects and false opening of tampering with electronic information.It can be said that the understanding and application of the first paragraph of Article 10 of the judicial interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate.It is the key to accurate conviction.
According to the author's observation,Lawyers generally believe that it is difficult to understand and apply the judicial interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate.There is a lot of controversy. Fortunately, in April this year, the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate published official articles respectively.The new four types of crimes of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT are interpreted to a certain extent.This paper will combine the viewpoints of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate to analyze the differences and shortcomings.It tries to accurately grasp the original intention of the rules of the crime of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT, and to find out the entry and exit criteria of the crime of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT.To explore the influence of the judicial interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate on the judicial practice of false opening cases.
The first type of behavior: the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate have the same view on "falsely opening without goods".
Paragraph 1 (1) of Article 10 of the judicial interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate:Issuing special invoices for value-added tax or other invoices used to defraud export tax rebates or tax deductions.
For the first type of false opening, the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate have the same views on the interpretation of the article.All of them are summed up as the behavior of "false opening without goods".The article of the Supreme People's Procuratorate points out that the "false opening without goods" without actual business is a typical false opening behavior.The article of the Supreme People's Court did not give a special explanation and explanation for "false opening without goods".However, in judicial practice, there is a lack of unified understanding and effective standards to judge whether there is actual business.The seemingly simple question of whether there is actual business is actually very complicated.In some specific industries and fields as well as innovative business models, market participants are often easily accused of having no actual business.For example, in the renewable resources industry, the car-free carrier industry, the flexible employment industry, the market-based procurement business in the field of bulk commerce and trade, and the non-logistics transportation.Transfer of cargo rights, affiliated business, advance payment by private account before settlement by public account, etc.The articles of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate do not focus on how to judge the existence of actual business.There are some gaps in regulating and guiding judicial practice, if we can give more clear and clear opinions.It can more effectively limit the crime circle of this crime, so as not to let "no goods open" negate the new format and wear down the innovative consciousness.
The 2nd kind of behavior: Have goods falsely to open, exceed tax amount falsely to open, which kind of expression is more accurate?
Item (2) of Paragraph 1 of Article 10 of the Judicial Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate:However, the issuance of special VAT invoices exceeding the corresponding tax of the actual business that should be deducted, and other invoices used to defraud export tax rebates and tax deductions.Of the ticket.For the second type of false opening behavior, the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate interpret the views of the article, showing a tendency to fight, specifically:
Interpretation of the article of the Supreme People's Procuratorate: The second item stipulates that if there is actual business but exceeds the corresponding tax of the actual business that should be deducted, "the goods are falsely issued."The essence of the excess part is also empty.
Interpretation of the article of the Supreme People's Court: "False opening of goods" means that although there is a real transaction,However, the deductible tax amount on the invoice exceeds the actual deductible tax amount.Including purchasing goods at a price excluding tax and obtaining invoices from third parties to deduct costs.
First of all, we need to be sure.Compared with the expression of "issuing special VAT invoices with false quantity or amount" in Fa Fa [1996] No.30,The judicial interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate defines the second type of false issuance as "issuing more than the actual deduction"."Business corresponding tax" is more accurate, which highlights that the legislative purpose of this crime is to protect the state tax.Not whether the invoice is accurate or not.That is to say, the false opening of goods is not the same as the staggered opening of goods, the former implies the consequences of tax fraud.For example, there is an actual transaction of 1 million yuan between the parties, and the invoice of 1.2 million yuan or 800000 yuan is not true.However, issuing an invoice of 800000 yuan does not cause tax losses and does not constitute a false crime.Therefore, the author believes that the abbreviation of the second category of criminal acts as "false opening of goods" is not accurate enough to reflect the original intention of the rules.It is more appropriate to call it "falsely issuing tax in excess of tax amount" for short, which can more accurately reflect the constituent elements of this crime.
Secondly, the Supreme People's Court defines the subject of false invoicing as a third party, which deviates from the subject and is inappropriate.From the interpretation articles of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate, we can see the differences of views.The Supreme People's Procuratorate has not broken through the logic of the combination of the trader and the drawer.The second kind of false opening behavior is interpreted as the main body has not deviated from the goods.The Supreme People's Court has incorporated the third-party invoicing situation into the second category of acts.It is believed that the second type of false invoicing includes the third party invoicing with more goods and tax-free transactions that the subject does not deviate from.The view of the Supreme People's Court is easy to cause confusion in the interpretation of the law.The situation in which the trader and the drawer are separated should not be included in the regulation of the second type of false issuance.
Finally, The Supreme People's Court's view that "the invoice taken from a third party to deduct the cost of purchasing goods without tax price" constitutes a false statement is wrong in itself.Yes.This view can be traced back to Judge Yao Longbing of the Supreme People's Court in 2019, published in the People's Court Daily, "On the" Goods "Type of False Opening Increase"The article on the nature of the act of special invoice for value tax points out that:
"The premise for the actor to apply for tax deduction is that he has paid the tax.". Only by paying taxes can we offset them, and it is impossible to offset taxes without paying taxes.Take physical transactions in practice as an example.In practice, when some units or individuals purchase goods, they agree with the seller that they do not need invoices as a transaction condition.Goods are purchased at the so-called low price without tax.After that, the purchaser obtains the input invoice from the third party and declares the deduction to the tax authorities to "reduce the cost".In this case, because the purchaser did not pay taxes in the purchase link, he could not enjoy the right of deduction.Most of the invoices obtained from third parties are purchased invoices, and they apply to the state for tax deduction.Essentially, it reduces its own cost by taking the national value-added tax.It is an act of transferring part of its transaction costs to the state.It is essentially no different from the act of using special VAT invoices to collect state tax without goods.Of course, this kind of behavior should be recognized as the act of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT to defraud the state tax.
The author believes that the above view is a misunderstanding of "price without tax".Taking the case of tax evasion at gas stations as an example, gas stations collect sales revenue through private households without invoicing at a low price.After investigating and dealing with gas stations, the tax Bureau will calculate the amount of private receipts, and when collecting taxes, the amount of receipts will be recognized as tax-inclusive income.The tax is calculated by converting "tax-inclusive price = tax-exclusive price * (1 + VAT rate)" into tax-exclusive income.The following tax documents sharing a case of tax evasion at a gas station can prove the above view of the author.It further confirms the mistake of the Supreme People's Court's view of so-called tax-free transactions.

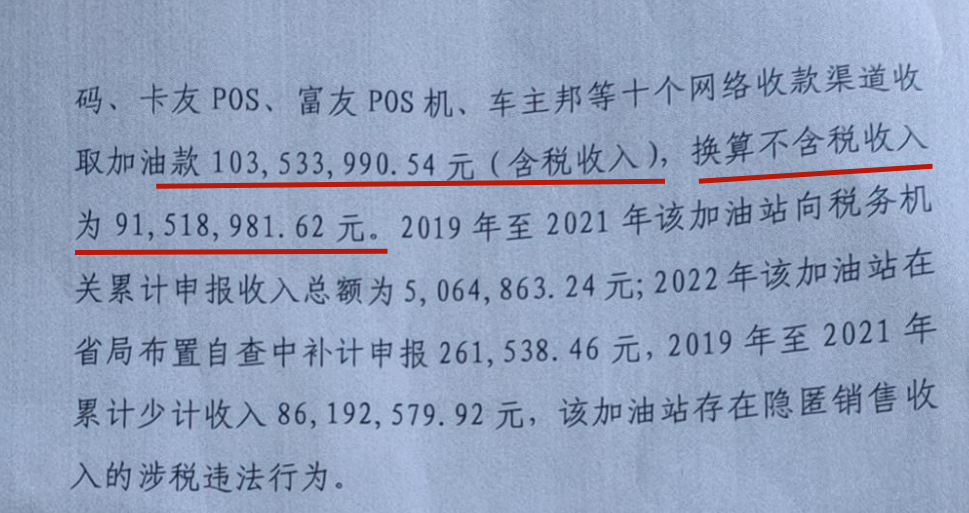
Based on this, the author believes that the following conclusions can be drawn: First, from the perspective of the taxation logic of tax authorities and the regulation of VAT law,As long as taxable acts occur, tax obligations arise, and all transaction prices are tax-inclusive.Secondly, the tax-free price agreed between the parties has no significance in the calculation of VAT tax.That is to say, the agreement on the price excluding tax between the two parties can not exempt the seller from tax liability.Thirdly, as long as the buyer pays the money, he has the corresponding right to deduct.If the invoice obtained from a third party in order to realize the right of deduction does not exceed the actual amount of tax to be deducted, it shall not be deemed as causing the loss of state tax.Therefore, the agreement does not include the tax price transaction settlement, but the purchaser still bears the tax price, and still enjoys the legitimate rights and interests of deduction.
What needs to be emphasized here is that the realization of deduction rights and interests in criminal law is not equal to the realization of deduction rights and interests in tax law.According to the Provisional Regulations on Value-added Tax and other provisions, four conditions should be met for tax deduction.First, the purchaser is a general taxpayer, second, the taxable items are purchased, third, the input tax is paid, and fourth, the invoice is obtained from the seller.。 For those who do not meet one of the above four conditions, it belongs to the business that can not deduct tax according to law.In the sense of tax law, the realization of deduction rights and interests requires tax payment and the issuance of invoices that can be deducted;The judgment from the perspective of criminal law should start from the essence, for the buyer, as long as the payment is the tax-inclusive price.Whether there is tax payment involves when the seller makes tax declaration, which is beyond the control of the buyer.If the realization of the deduction rights and interests is based on the actual tax payment, it is unfair to the buyer, and the buyer can deduct the business according to law.Because the other party can not invoice and find a third party to invoice for tax deduction, as long as it has the actual purchase to obtain the rights and interests of deduction.If it does not exceed the scope of the deduction rights and interests obtained, it will not be recognized as causing the loss of state tax.This is a deduction act with the rights and interests of deduction in criminal law, and the perpetrator does not have the purpose of defrauding tax.It does not directly cause the loss of state tax revenue.
Can't all the acts that have the rights and interests of deduction in criminal law be imputed? Apparently not.The article of the Supreme People's Court points out that "taxpayers are within the scope of their taxable obligations."In order to pay less tax, the deduction is made by falsely increasing the input, even if the means of false deduction is adopted.However, according to the principle of unity of subjectivity and objectivity, it should be punished as the crime of tax evasion.This is also one of the provisions of Article 1, Paragraph 1, Item 3 of the Interpretation that "falsely offset the input tax" is one of the "means of deception and concealment" of the crime of tax evasion.Consideration of. It can be seen that the act of falsely issuing tax credits without tax law but with the rights and interests of deduction in criminal law should be defined as tax evasion.For example, opposite opening and ring opening do not constitute false opening, but constitute tax evasion.The Supreme People's Court here affirms the distinction between the crime of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT and the crime of tax evasion.However, the expression of "scope of taxable obligation" is not clear, and it is more accurate to interpret it as "scope of tax deduction" or "scope of rights and interests deduction".
The third type of behavior: the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate have obvious differences in their views.
Item (3) of Paragraph 1 of Article 10 of the Judicial Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate: For businesses that cannot deduct taxes according to lawIssuing special VAT invoices or other invoices used to defraud export tax rebates or tax deductions by fabricating transaction subjects.For the third type of false opening, the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate have a thorough fight. Let's see:
Interpretation of the article of the Supreme People's Procuratorate: Item 3 refers to the suggestions of the Ministry of Public Security and the State Administration of Taxation.In practice, the drawee of the actual transaction does not meet the conditions for deduction.However, it is also a false act to deduct the invoice by fabricating a third party unrelated to the transaction.
Interpretation of the article of the Supreme People's Court: "Fictitious transaction subject type is falsely opened".It is mainly aimed at the drawee who can not be deducted according to the law, through the fictitious transaction subject, the fictitious subject can deduct the tax.So as to realize the false opening of tax fraud.
The view of the Supreme People's Procuratorate is obviously to interpret the third type of behavior as a substitute behavior.That is to say, the Supreme People's Procuratorate considers that issuing invoices on behalf of others also constitutes a criminal act of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT.More importantly, the article of the Supreme People's Procuratorate explains that the source of this article is the proposal of the Ministry of Public Security and the General Administration of Taxation.In practice, public security organs and tax authorities often investigate and deal with the situation of issuing invoices on behalf of others.Therefore, the interpretation of the Supreme People's Procuratorate may be more accurate.
However, the author believes that the views of the Supreme People's Procuratorate are suspected.It equates "not deductible according to law" with "not meeting the conditions for deduction".The latter corresponds to generation opening, while the former corresponds to special generation opening.The judicial interpretations of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate only define special acts as criminal acts.It does not define the general act of opening on behalf of others as a criminal act, which is more in line with the purpose of limiting the criminal circle.The so-called special agent is the business that does not allow tax deduction according to the provisions of VAT.For example, wages are not allowed to deduct taxes according to law.Tax deduction by issuing VAT invoices by a third party is a special substitute for the third type of false issuance, which should be regulated.The Supreme People's Procuratorate interprets the special act as a general act, which is an expanded understanding of the criminal circle.General agent issuance should not be included in the consideration of crime, for example, the documents of the General Administration stipulate that affiliated invoicing is legal.Invoicing by affiliation is a general act of issuing on behalf of others, including agreement affiliation, oral affiliation and factual affiliation.In addition, although the special agent constitutes a crime, there is also the possibility of committing a crime.Whether a crime can be convicted or not depends on whether the clause of conviction can be applied according to the specific circumstances.
The views of the Supreme People's Court are unintelligible. The drawee can not deduct the tax and let the fictitious subject deduct the tax.The author has hardly seen such a situation in the defense practice of false cases.Therefore, the view of the Supreme Court is neither logical nor divorced from the practice of false invoicing cases, so we will not make too much analysis here.
The falsification of electronic invoice information needs further test in judicial practice.
Item (4), Paragraph 1, Article 10 of the Judicial Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate: illegally tampering with special VAT invoices orElectronic information related to other invoices used to defraud export tax rebates and tax deductions.
For the fourth category of false invoices, the article of the Supreme People's Procuratorate points out that "the fourth item is a provision for the electronic management of invoices.".At present, the special VAT invoice has been managed electronically, and the special VAT invoice does not need to be deducted by paper.Tax authorities only need to compare and confirm the electronic information of invoices, and deduct them if they meet the conditions for deduction.Therefore, the nature and harmfulness of illegally tampering with electronic invoice information is comparable to that of falsely issuing paper VAT special invoices.Belon to a novel false opening behavior.The article of the Supreme People's Court holds that the fourth type of false opening is in line with the construction and implementation of the "Golden Tax Phase IV" system.Tax collection and management has changed from tax control by ticket to tax control by number. The author believes that this kind of false crime is rare in practice.Whether it can effectively limit the crime circle still needs to be further tested by judicial practice.
Conclusion: The promulgation of the judicial interpretation of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate has declared the 205th criminal law in the future.The article is no longer amended, but also declares that the interpretation of the provisions of the Criminal Law has formally entered a new period.No Matt whether that judicial interpretation of the Supreme people's court and the Supreme people's procuratorate are satisfactory,Regardless of the differences between the views of the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate,It will guide and standardize the judicial practice in the next ten, twenty or even longer years.Can local judicial organs go from understanding the rules to applying the rules to adapting to the rules and finally to abiding by the Supreme People's Court and the Supreme People's Procuratorate?It is worth observing the spirit of the court to limit the criminal circle of this crime.The criminal act clause of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT is the most important content in the criminal rule system of falsely issuing special invoices for VAT.It will certainly become the main battlefield of the prosecution, defense and trial.In such a variety of complex disputes, perhaps only by closely following the basic theory and rules of the constitutive elements of a false crime,In order to walk out of a road of hope.