Spiritual work platform on behalf of the executive remuneration is characterized as illegal sale of VAT invoices crime should be how to break the situation?
Editor's Note: The two high tax-related judicial interpretations make it clear that the crime of false invoicing is not punishable if the purpose is not to fraudulently offset the tax, and if there is no fraudulent loss of tax due to offsetting. At the same time, the interpretation of the Supreme Law pointed out that the behavior of invoicing party charging “invoicing fee” and “tax point” and then invoicing others is essentially selling VAT invoices as commodities, and it is an illegal sale of VAT invoices. Influenced by this, the cases involving platform enterprises are basically characterized according to the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices. According to the main data of judicial trial work in the first half of this year published by the Supreme Court, the number of cases received in the first instance for the crime of illegal sale of VAT invoices increased by 190% year-on-year, which also reflects a significant shift in the judicial thinking of handling cases involving invoices. This article intends to combine a real case to analyze how the enterprises involved in the case should break the situation.
I. Introduction of the case: a spiritual labor platform for executives to pay remuneration for illegal sale of public prosecution
(I) Basic facts of the case
A person controls and operates A flexible labor platform, during the period from 2020 to 2022, A platform obtains the qualification of entrusted levy, externally declares that it can solve the problems of public-to-private transfer and expense settlement for enterprises, and lets the enterprises upload the information of personnel and labor scenarios by themselves after registering on the platform, etc. During the period involved in the case, the A platform issues remuneration for the executives of a number of enterprises under the name of flexible labor, and issues 5,000 VAT invoices, more than 5,000, with a total price and tax of 5,000,000 yuan. more than 580 million yuan in price and tax, with a total tax amount of more than 30 million yuan.
(II) Opinions of the Procuratorial Authorities
The procuratorial authorities held that Defendant A was unable to confirm the real situation of employment personnel and employment scenarios on Platform A. Under the guise of paying services on behalf of the employees, he took the way of signing false service agreements and making false fund flows to sell VAT invoices to a number of enterprises and charge the invoicing fees of the enterprises, and he prosecuted Defendant A in the People's Court for the crime of unlawful sale of VAT invoices.
(III) Case Commentary
At present, the conviction and sentencing of cases involving invoices on the Lingong platform has quietly changed, and the criminal risk of characterizing the invoicing behavior of the Lingong platform with the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices has dramatically increased, which is specifically manifested in the following:
-
the burden of proof of the procuratorate is greatly reduced
Before the introduction of the two high tax-related judicial interpretations, the procuratorial authorities in such cases were prosecuted to the court for the crime of fraudulently issuing VAT invoices, and in the judicial decision, the court often found that the crime needed to be constituted with the purpose of fraudulently offsetting taxes and the result of causing tax losses, and the procuratorial authorities proved that there was a fraudulent issuance of invoices on the platform of the Lingong Group and that it was well aware of the fact that the recipient enterprises had obtained VAT invoices for fraudulently offsetting taxes and that there was a criminal risk of fraudulently issuing VAT invoices to the recipient enterprises. The procuratorial authorities shall prove that the platform has engaged in the act of false opening, knows that the invoiced enterprise has obtained the VAT invoice for the purpose of fraudulently offsetting the tax, and has conspired with the invoiced enterprise to fraudulently offset the state tax by means of the false opening of the VAT invoice, and the specific amount of the loss of tax. After the introduction of the two high tax-related judicial interpretations, the procuratorial authorities of such cases filed a public prosecution with the court for the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices, which is a behavioral crime, as long as the perpetrator exists in the act of illegally selling, that is, it constitutes the crime, and at the same time the article of the Supreme Court has had a significant impact on the judicial decision-making, and the procuratorial authorities can no longer take evidence on the invoicing behavior on Linggong's platform for the invoicing and the recipient of invoices to cheat the tax together at this stage. The procuratorial authorities can no longer take evidence on the existence of joint fraudulent tax offsetting between the invoicing party and the invoiced party, as long as the platform receives money from the invoiced party, it can be accused that the platform issues VAT invoices as commodities to the invoiced party, which lowers the threshold of conviction in this kind of case.
-
Easier to be prosecuted by public security organs
According to the Provisions of the Supreme People's Procuratorate and the Ministry of Public Security on the Criteria for Filing Criminal Cases under the Jurisdiction of the Public Security Organs (II), the public security organs can file a case for prosecuting the illegal sale of VAT invoices if the total amount of VAT is over 100,000 yuan, or the amount of VAT is over 10 copies of VAT invoices, the amount of VAT is over 60,000 yuan, and the amount of illegal profit is over 10,000 yuan, and the public security organs can file a case for prosecuting the illegal sale of VAT invoices. The public security organ can file a case for prosecution if the amount of tax in the special invoice for value-added tax is more than 100,000 yuan or the amount of loss of national tax is more than 50,000 yuan. It can be seen that the prosecution standard for illegal sale of VAT invoices is more lenient than the conditions for the crime of false opening of VAT invoices, and the public security organs can file a case once the amount of illegal profit made by the spiritual platform reaches more than 10,000 yuan.
-
It is easier to reach the sentencing standard of more than ten years.
According to the tax-related judicial interpretations of the two high courts, the illegal sale of VAT invoices with a face value of more than five million yuan or more than 500 copies with a face value of more than three million yuan, meeting any one of the conditions, that is, to reach a sentencing standard of more than ten years, while the amount of tax on the falsely issued VAT invoices reaches more than five million yuan to reach a sentencing standard of more than ten years.
Therefore, the prosecuting authority in this case has filed a public prosecution with the court for the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices, which is extremely unfavorable to the Lingong platform. The author believes that the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices should be traced back to examine the historical origin of this crime so as to break down the existing viewpoints of the judiciary.
II. Determination of the Crime of Illegal Sale of VAT Special Invoice from the Evolution of VAT Special Invoice Management
(I) The era of manually filling out blank VAT special invoices
According to the provisions of the Interim Measures for National Invoice Management (Cai Shui Zi [1986] No. 262, now invalid), taxpayers who have applied for tax registration shall firstly provide tax registration certificates or other certificates to the tax authorities and submit the report on the application for purchase of invoices, and after the tax authorities have completed the examination and approval, the taxpayers shall go through the procedures of purchase of invoices, and then the taxpayers shall manually fill out blank VAT special invoices on the blank VAT special invoices they have purchased according to the actual operation business situation. VAT invoices are then issued to the public by manually filling in the blank invoices purchased by the taxpayers according to their actual business operations. As shown in the figure:
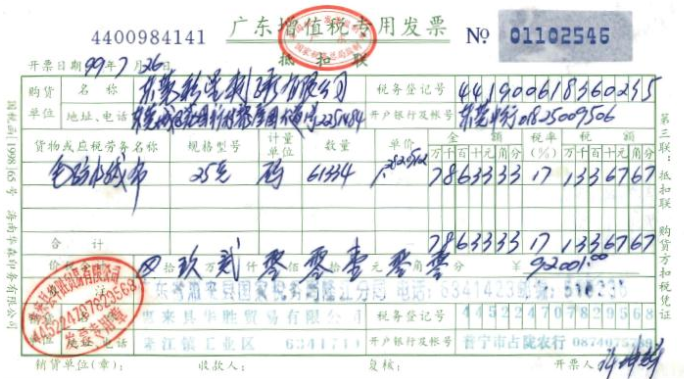
In the context of that time, due to the weak and low level of the state's ability to supervise VAT invoices, coupled with the fact that the tax authorities imposed restrictions on the number and amount of invoices to be purchased by taxpayers, in practice, where the purchase limit did not meet the needs of the enterprises, the enterprises might choose to purchase blank invoices from other enterprises, and as a result, there was a large number of sales of blank VAT invoices, which disrupted the state tax system. 1995 The Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (NPC) established the invoice crime cluster, and the 1997 Criminal Law basically absorbed the content of the 1995 NPC Standing Committee's decision, from which Article 207 of the Criminal Law arose. According to the Criminal Law Interpretation compiled by the Criminal Law Office of the Legal System Working Committee of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (NPCSC) in 1997, “the crime of illegal VAT invoices refers to the act of selling invoices by holders of VAT invoices in violation of the law except for VAT invoices issued by tax authorities in accordance with the regulations. ...... VAT special invoices are issued by the State tax authorities in accordance with the regulations and are restricted to general VAT taxpayers. Other than that, no one and no unit may sell them, and special VAT invoices must be managed very strictly”. Accordingly, the invoices sold by the tax authorities can only be blank VAT invoices, and it is impossible for them to sell the VAT invoices with the information of the purchaser, amount and quantity filled in to the taxpayers, and the VAT invoices purchased from the tax authorities can only be blank invoices for the perpetrators to sell to others.
At the same time, the Criminal Law stipulates the crimes of illegal sale of VAT invoices and false opening of VAT invoices, which precisely indicates that illegal sale and false opening belong to two completely different behaviors. At this time, if the perpetrator sells blank VAT invoices to others and does not participate in the subsequent false invoicing behavior, it constitutes the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices; if the perpetrator participates in the subsequent false invoicing behavior, it constitutes the crime of falsely issuing VAT invoices. It can be seen that the false invoicing of VAT constitutes one more act than the illegal sale of VAT invoices, which is also the reason why the crime of false invoicing of VAT constitutes one more death penalty than the crime of illegal sale of VAT invoices at that time.
In 1996, Qingdao Intermediate People's Court sentenced Chen Dongliang to 8 years' imprisonment for the crime of illegal sale of VAT invoices and Miao Fengjie to death for the crime of false opening of VAT invoices, which can also be proved by the fact that, in June 1994, Qingdao Yinsda Shopping Center Manager Chen Dongliang gave Zhang Hanlong 2 old million-yuan version of the invoices purchased by the shopping center and 3 new million-yuan version of the invoices to Zhang Hanlong, who brought 5 invoices to the south of Qingdao with Qingdao Huashan and sent the invoices to the south of Qingdao with the name of Qingdao Huashan. Special invoices to the south in the name of the Qingdao Overseas Chinese Company, engraved official seal, large-scale false open, illegal profiteering. in October, Zhang Hanlong invoice stubs to Chen Dongliang and paid 15,000 yuan. After that, Chen Dongliang's uncle Miao Fengjie knew the matter, took the initiative to contact Zhang Hanlong, first carried Qingdao Lide Protection Materials Co., Ltd. blank VAT invoices, industrial and commercial registration certificates, tax registration certificates, invoices purchasing certificates, and Zhang Hanlong flew to Shantou together to issue invoices, and then due to the company's business license of the business scope of the metal, the issuance of invoices is limited, Miao Fengjie and to carry the Qingdao Sifang Luhua Trading Company blank VAT invoices, industrial and commercial registration certificates, tax registration certificates, invoice purchase certificates with Zhang Hanlong. VAT invoices, business registration certificate, tax registration certificate, invoice purchase certificate, etc. to Shantou to Zhang Hanlong, by Zhang Hanlong to take away and issue invoices, Zhang Hanlong successively handed over a total of 9,800 yuan to Miao Fengjie. At the court at that time, the court did not adopt the defense that Miao Fengjie's behavior of not issuing VAT falsely did not constitute the crime of issuing VAT invoices falsely.
(II) The era of machine-printed blank VAT invoices
With the continuous improvement and upgrading of the Golden Tax System, manual invoicing has been completely canceled, and taxpayers are required to apply to the tax authorities for the paper invoice requisitioning formalities with the tax registration documents, identity certificates of the operators, and impressions of special invoice seals, etc. After the requisitioning has been completed, the taxpayers issue VAT invoices to the outside world through machine-typing according to the actual business. As shown in the figure:
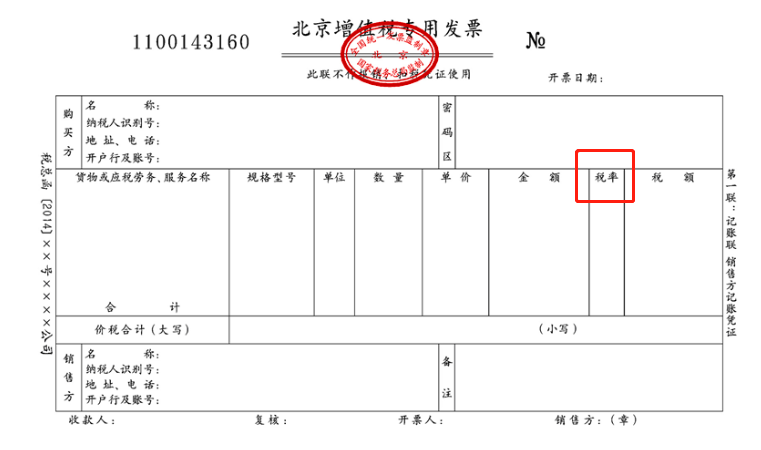
Against this background, there still exists the possibility that the perpetrator sells blank VAT invoices to others, who obtain the blank VAT invoices and then issue them to the outside world, and the perpetrator constitutes the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices, and if the perpetrator prints false purchaser information on the blank VAT invoices without a real transaction, etc., it constitutes the crime of falsely issuing VAT invoices.
This can also be confirmed in the case of Chen Lianchang et al. Crime of Illegally Selling VAT Invoice ((2019) Min 01 Criminal End No. 1449). In this case, the Court of Second Instance and the Court of First Instance both held that Defendant Chen Lianchang's act of selling 452 blank VAT invoices of 20 companies, including Fujian So-and-So Trading Company Limited, to Zhan Junhuan and others, and 60 blank VAT invoices of Fujian So-and-So Import and Export Trading Company Limited, with a total face amount of RMB 51.2 million yuan, to Zhan Dongzhou constituted the crime of unlawfully selling VAT invoices; The act of Defendant Chen Lianchang of hiring Defendant Zhan Junhuan to print invoices at RMB20 or RMB40 per copy in the absence of a genuine transaction and falsely issuing 1,337 VAT invoices in the name of Fujian So-and-So Trading Company Limited and 50 other companies for others with a tax amount of more than RMB22.4 million constitutes the crime of falsely issuing VAT invoices.
(iii) The era of electronic invoices and digital electronic invoices
With the nationwide implementation of the VAT electronic invoice system on January 1, 2016, taxpayers can no longer issue paper VAT invoices to the outside world, and the gradual disappearance of blank VAT invoices, as well as with the release of the “Announcement of the State Administration of Taxation of the Tibet Autonomous Region Taxation Bureau on the Pilot Work of Comprehensively Digitized Electronic Invoices,” the digital and electric invoices have now been covering the whole country, and the tax authorities no longer conduct Invoice ticket type approval and invoice collation, and taxpayers can issue invoices through the e-invoice service platform after identity verification through real-person authentication and other means.
So far, in the era of electronic invoices and digital invoices, taxpayers no longer need to take the initiative to apply for blank VAT invoices from tax authorities to issue invoices. In the current era of digital invoices, taxpayers are no longer subject to the limitations on the number of invoices issued and the maximum invoicing amount, and as long as they are in the total amount of the credit granted to them, they can issue their own invoices according to their actual needs, so applying for blank VAT invoices is no longer a prerequisite for the issuance of VAT invoices. Therefore, applying for blank VAT invoices is no longer a precondition for issuing VAT invoices, and taxpayers who sell blank VAT invoices to others no longer have the space for application. Therefore, illegal sale of VAT invoices should be in the same pace with the development of the society, and the crime should be abolished in the current situation of the rule of tax by numbers.
Even from the point of view of the article of the Supreme Court, the cases involving invoices of platform enterprises should not be characterized as illegal sale.
The article of the Supreme Court pointed out that, for the invoicing party, if it cannot be proved that there is a common intention between the invoiced party and the invoiced party, the behavior of invoicing others after collecting “invoicing fee” and “tax point” is essentially treating the VAT invoices as commodities for sale, and it is an illegal sale of VAT invoices. The act of issuing VAT invoices for others after “invoicing fee” and “tax point” is essentially selling VAT invoices as commodities, which is illegal sale of VAT invoices. The main reason is that in practice, the invoicing party is mostly a shell company without actual business behavior, and its invoicing business must be strictly combated; in practice, the invoicing party and the invoiced party trade more and more through the network, and the invoicing party mostly belongs to the type of invoicing of “all comers are not refused”, and it is not consistent with the objective reality that the invoiced party and the invoiced party face the difficulty of evidence collection, nor is it consistent with the objective reality that the invoiced party and the invoiced party are jointly intentional. It is not only difficult to obtain evidence, but also inconsistent with the objective reality. However, if the invoicing party, such as Lingong Platform, can prove that it is not a shell company and has carried out actual business, and at the same time, it has carefully screened the counterparties, fulfilled the obligation of backtesting to the maximum extent, and selected a fixed number of enterprises with which to carry out business, it can be proved that the Lingong Platform type of enterprises is not a “refusing all comers” type of invoicing, and that it does not let the invoiced party cheat tax credits. There is no subjective willfulness of letting the invoiced party cheat the tax.
As for the present case, Lingong Platform A is not an empty shell enterprise, but actually carries out business, and does not sell blank VAT invoices to enterprises, which should not be characterized as the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices. In fact, without verifying the employment scenario and other information, the Lingong Platform issues remuneration for the executives of the enterprise and issues VAT invoices that do not conform to the actual situation, which belongs to the behavior of false invoicing, and it is a false invoicing behavior if the Lingong Platform is able to prove that it has no relationship with the recipient. If Lingong Platform can prove that it did not conspire with the recipient enterprise to fraudulently offset the tax, did not let the downstream enterprise fraudulently offset the tax intentionally, and did not cause the loss of fraudulently offsetting the tax, it cannot be characterized as the crime of fraudulently issuing VAT invoices. However, this act of Lingong Platform did infringe the legal interests of invoice management order, and it can be investigated for the crime of fraudulently issuing invoices and be held criminally liable for the crime.
III.Even from the point of view of the article of the Supreme Court, the cases involving invoices of platform enterprises should not be characterized as illegal sale.
The article of the Supreme Court pointed out that, for the invoicing party, if it cannot be proved that there is a common intention between the invoiced party and the invoiced party, the behavior of invoicing others after collecting “invoicing fee” and “tax point” is essentially treating the VAT invoices as commodities for sale, and it is an illegal sale of VAT invoices. The act of issuing VAT invoices for others after “invoicing fee” and “tax point” is essentially selling VAT invoices as commodities, which is illegal sale of VAT invoices. The main reason is that in practice, the invoicing party is mostly a shell company without actual business behavior, and its invoicing business must be strictly combated; in practice, the invoicing party and the invoiced party trade more and more through the network, and the invoicing party mostly belongs to the type of invoicing of “all comers are not refused”, and it is not consistent with the objective reality that the invoiced party and the invoiced party face the difficulty of evidence collection, nor is it consistent with the objective reality that the invoiced party and the invoiced party are jointly intentional. It is not only difficult to obtain evidence, but also inconsistent with the objective reality. However, if the invoicing party, such as Lingong Platform, can prove that it is not a shell company and has carried out actual business, and at the same time, it has carefully screened the counterparties, fulfilled the obligation of backtesting to the maximum extent, and selected a fixed number of enterprises with which to carry out business, it can be proved that the Lingong Platform type of enterprises is not a “refusing all comers” type of invoicing, and that it does not let the invoiced party cheat tax credits. There is no subjective willfulness of letting the invoiced party cheat the tax.
As for the present case, Lingong Platform A is not an empty shell enterprise, but actually carries out business, and does not sell blank VAT invoices to enterprises, which should not be characterized as the crime of illegally selling VAT invoices. In fact, without verifying the employment scenario and other information, the Lingong Platform issues remuneration for the executives of the enterprise and issues VAT invoices that do not conform to the actual situation, which belongs to the behavior of false invoicing, and it is a false invoicing behavior if the Lingong Platform is able to prove that it has no relationship with the recipient. If Lingong Platform can prove that it did not conspire with the recipient enterprise to fraudulently offset the tax, did not let the downstream enterprise fraudulently offset the tax intentionally, and did not cause the loss of fraudulently offsetting the tax, it cannot be characterized as the crime of fraudulently issuing VAT invoices. However, this act of Lingong Platform did infringe the legal interests of invoice management order, and it can be investigated for the crime of fraudulently issuing invoices and be held criminally liable for the crime.