Coal Industry Tax Compliance Report(2024)
The characteristics of China's energy resources, with abundance in coal, scarcity in oil, and limited natural gas, have shaped a predominant energy consumption structure centered around coal. Coal, as a fundamental energy source in China, accounts for over half of the energy consumption and holds a crucial strategic position in the national economy. In the realm of taxation, recent years have witnessed diverse and multi-stage tax risks in the coal industry. Tax-related issues during the operation of coal enterprises have become increasingly prominent, leading to numerous challenges in tax compliance.
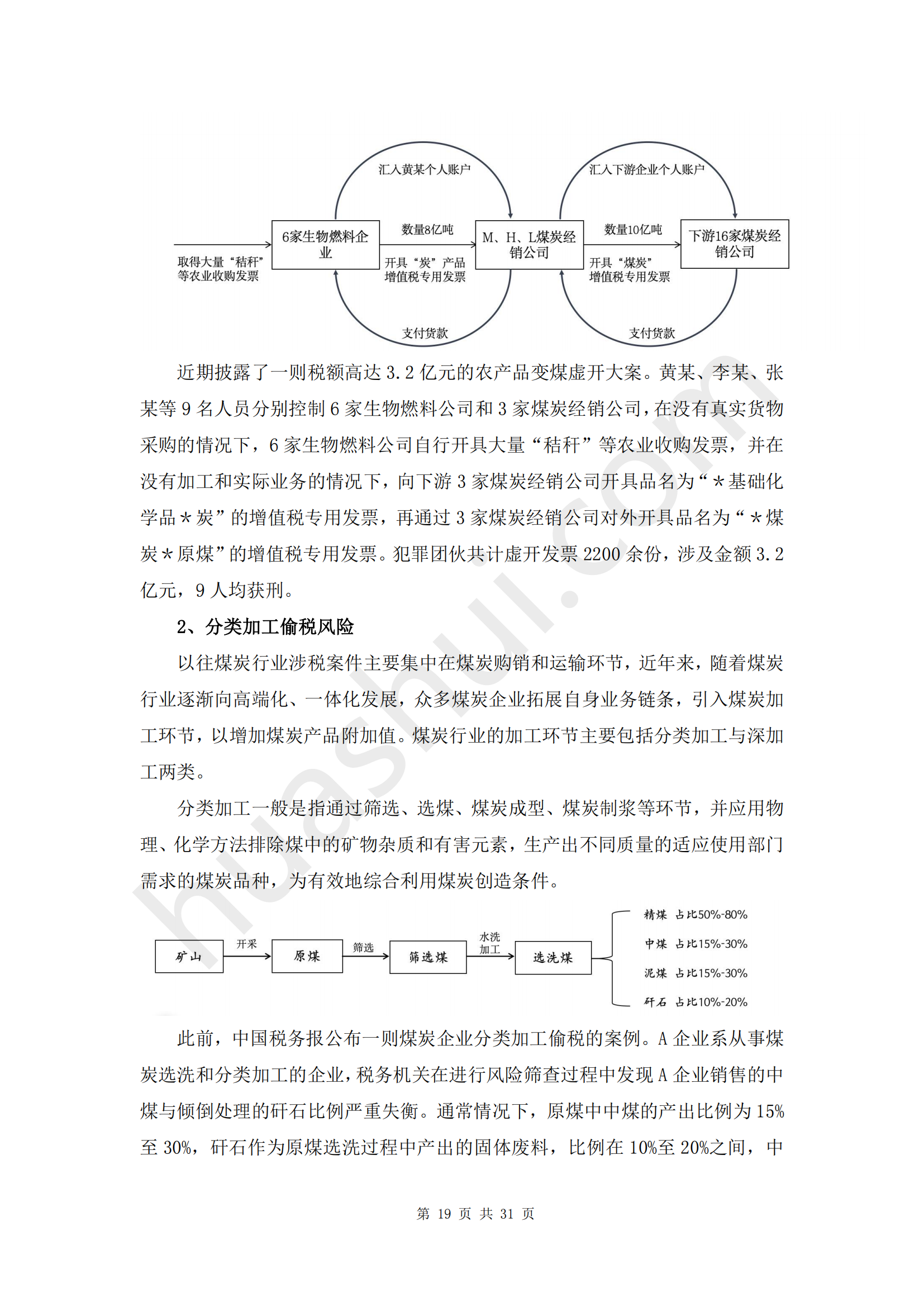
Against the backdrop of coal mining quotas, coal enterprises often resort to off-the-books operations to sell coal extracted beyond the allocated quotas. Downstream coal trading enterprises, when purchasing coal from these enterprises, face challenges in obtaining value-added tax (VAT) special invoices for VAT input deduction and as evidence for corporate income tax prepayment. Simultaneously, the frequent mergers and acquisitions in the coal industry in recent years have limited the quantity of coal that trading enterprises can purchase from officially authorized large mines within the quotas. To meet the coal demand of downstream enterprises, coal trading companies are compelled to procure over-quota coal from small mines, intensifying the invoicing challenges in the coal industry due to macroeconomic fluctuations. In an attempt to address the insufficient deduction of input invoices, some coal enterprises have revamped their business models, utilizing methods such as affiliation and outsourced invoicing to obtain input invoices. However, due to the diversity and complexity of these models, coupled with differing interpretations by tax authorities, there is a significant risk of false invoicing. With the intensification and institutionalization of the "anti-fraud and anti-deception" special campaign, the coal industry has experienced a surge in cases involving fraudulent invoicing and tax evasion. Companies and their executives face administrative and even criminal liabilities.
Beyond invoicing issues, the coal industry has witnessed numerous cases of resource tax evasion during the extraction process, consumption tax evasion during processing, and income tax evasion during equity changes in recent years. The tax risks in the coal industry are gradually extending to multiple stages and tax types.
In judicial practice, publicly disclosed cases of coal enterprises engaging in fraudulent invoicing in 2023 reveal instances where recipient enterprises were penalized for tax evasion without being referred to public security authorities, as well as cases where retrials resulted in acquittal for circular invoicing and counter-invoicing behaviors. As the nationwide reform of the criminal compliance mechanism by the procuratorate unfolds, several local courts are conducting compliance pilot programs during the trial phase. These changes present new opportunities for legal defense in tax-related criminal cases in the coal industry. Based on these developments and our extensive observation of the coal industry, as well as our experience in representing coal enterprises in tax-related criminal cases, Huatax has prepared this report. The report delves into the tax environment of the coal industry under the new tax administration situation, consolidates the latest tax-related criminal and administrative cases involving coal enterprises in 2023, elucidates the current status, causes, and recent changes in tax-related criminal risks in the coal industry. Furthermore, based on this analysis, the report provides recommendations for enterprise management compliance, aiming to assist coal enterprises in proactively managing tax risks, strengthening internal risk control and external risk isolation, and effectively addressing and mitigating tax-related legal risks.
Click to download:《Coal Industry Tax Compliance Report》(2024)